Tag: electricity
What is a fuel cell and how will they help power the future?
How do you get a drink in space? That was one of the challenges for NASA in the 1960s and 70s when its Gemini and Apollo programmes were first preparing to take humans into space.
The answer, it turned out, surprisingly lay in the electricity source of the capsules’ control modules. Primitive by today’s standard, these panels were powered by what are known as fuel cells, which combined hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity. The by-product of this reaction is heat but also water – pure enough for astronauts to drink.
Fuel cells offered NASA a much better option than the clunky batteries and inefficient solar arrays of the 1960s, and today they still remain on the forefront of energy technology, presenting the opportunity to clean up roads, power buildings and even help to reduce and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from power stations.
Power through reaction
At its most basic, a fuel cell is a device that uses a fuel source to generate electricity through a series of chemical reactions.
All fuel cells consist of three segments, two catalytic electrodes – a negatively charged anode on one side and a positively charged cathode on the other, and an electrolyte separating them. In a simple fuel cell, hydrogen, the most abundant element in the universe, is pumped to one electrode and oxygen to the other. Two different reactions then occur at the interfaces between the segments which generates electricity and water.
What allows this reaction to generate electricity is the electrolyte, which selectively transports charged particles from one electrode to the other. These charged molecules link the two reactions at the cathode and anode together and allow the overall reaction to occur. When the chemicals fed into the cell react at the electrodes, it creates an electrical current that can be harnessed as a power source.
Many different kinds of chemicals can be used in a fuel cell, such as natural gas or propane instead of hydrogen. A fuel cell is usually named based on the electrolyte used. Different electrolytes selectively transport different molecules across. The catalysts at either side are specialised to ensure that the correct reactions can occur at a fast enough rate.
For the Apollo missions, for example, NASA used alkaline fuel cells with potassium hydroxide electrolytes, but other types such as phosphoric acids, molten carbonates, or even solid ceramic electrolytes also exist.
The by-products to come out of a fuel cell all depend on what goes into it, however, their ability to generate electricity while creating few emissions, means they could have a key role to play in decarbonisation.
Fuel cells as a battery alternative
Fuel cells, like batteries, can store potential energy (in the form of chemicals), and then quickly produce an electrical current when needed. Their key difference, however, is that while batteries will eventually run out of power and need to be recharged, fuel cells will continue to function and produce electricity so long as there is fuel being fed in.
One of the most promising uses for fuel cells as an alternative to batteries is in electric vehicles.
Rachel Grima, a Research and Innovation Engineer at Drax, explains:
“Because it’s so light, hydrogen has a lot of potential when it comes to larger vehicles, like trucks and boats. Whereas battery-powered trucks are more difficult to design because they’re so heavy.”
These vehicles can pull in oxygen from the surrounding air to react with the stored hydrogen, producing only heat and water vapour as waste products. Which – coupled with an expanding network of hydrogen fuelling stations around the UK, Europe and US – makes them a transport fuel with a potentially big future.
Fuel cells, in conjunction with electrolysers, can also operate as large-scale storage option. Electrolysers operate in reverse to fuel cells, using excess electricity from the grid to produce hydrogen from water and storing it until it’s needed. When there is demand for electricity, the hydrogen is released and electricity generation begins in the fuel cell.
A project on the islands of Orkney is using the excess electricity generated by local, community-owned wind turbines to power a electrolyser and store hydrogen, that can be transported to fuel cells around the archipelago.
Fuel cells’ ability to take chemicals and generate electricity is also leading to experiments at Drax for one of the most important areas in energy today: carbon capture.
Turning CO2 to power
Drax is already piloting bioenergy carbon capture and storage technologies, but fuel cells offer the unique ability to capture and use carbon while also adding another form of electricity generation to Drax Power Station.
“We’re looking at using a molten carbonate fuel cell that operates on natural gas, oxygen and CO2,” says Grima. “It’s basic chemistry that we can exploit to do carbon capture.”
The molten carbonate, a 600 degrees Celsius liquid made up of either lithium potassium or lithiumsodium carbonate sits in a ceramic matrix and functions as the electrolyte in the fuel cell. Natural gas and steam enter on one side and pass through a reformer that converts them into hydrogen and CO2.
On the other side, flue gas – the emissions (including biogenic CO2) which normally enter the atmosphere from Drax’s biomass units – is captured and fed into the cell alongside air from the atmosphere. The CO2and oxygen (O2) pass over the electrode where they form carbonate (CO32-) which is transported across the electrolyte to then react with the hydrogen (H2), creating an electrical charge.
“It’s like combining an open cycle gas turbine (OCGT) with carbon capture,” says Grima. “It has the electrical efficiency of an OCGT. But the difference is it captures CO2 from our biomass units as well as its own CO2.”
Along with capturing and using CO2, the fuel cell also reduces nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions from the flue gas, some of which are destroyed when the O2and CO2 react at the electrode.
From the side of the cell where flue gas enters a CO2-depleted gas is released. On the other side of the cell the by-products are water and CO2.
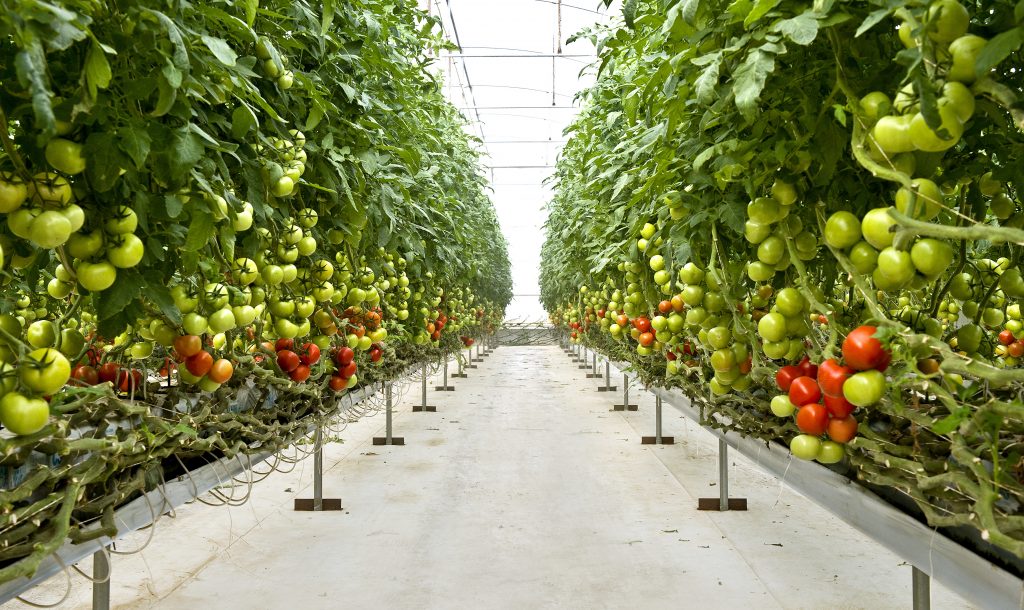

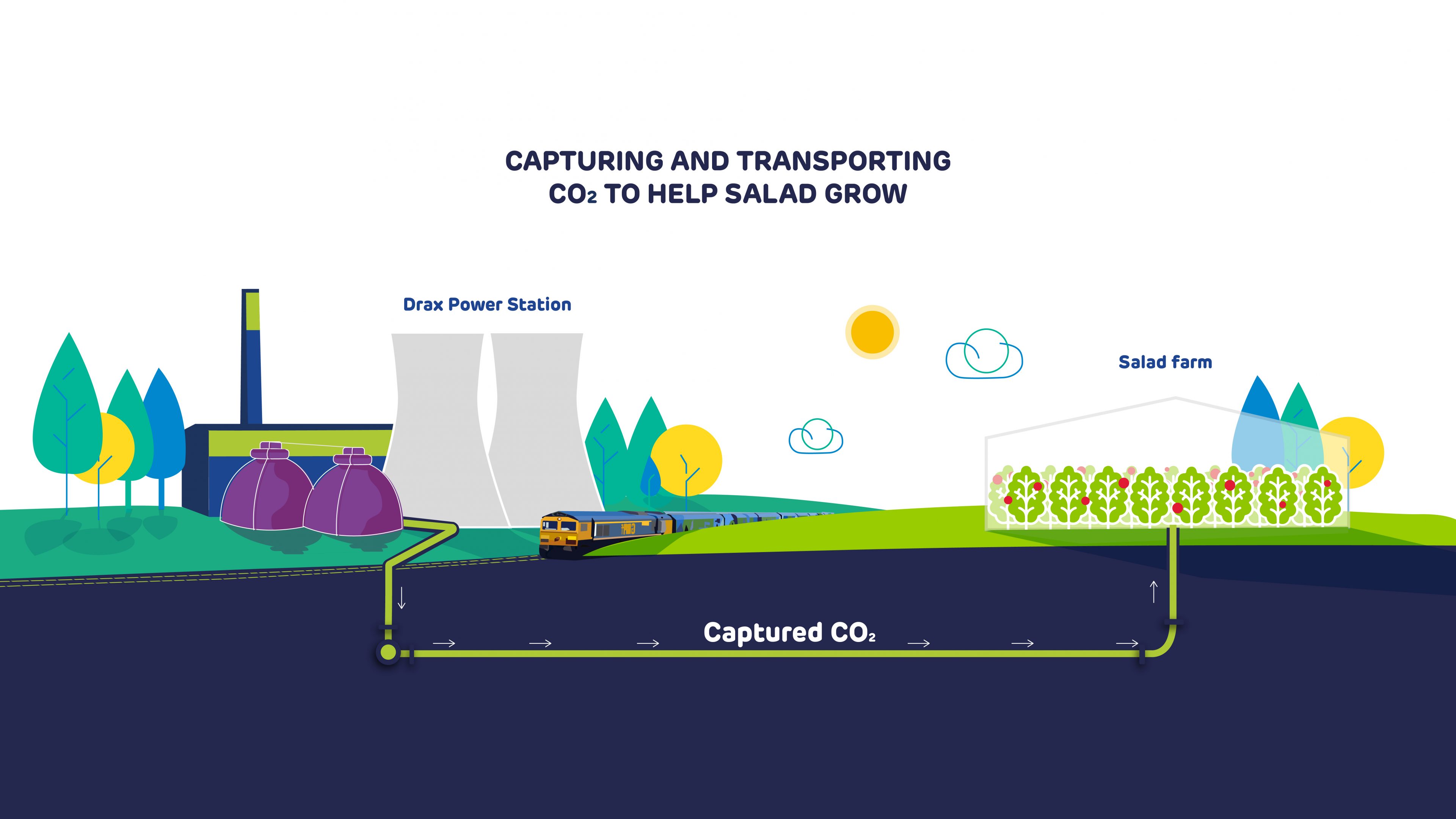
During a government-supported front end engineering and design (FEED) study starting this spring, this CO2 will also be captured, then fed through a pipeline running from Drax Power Station into the greenhouse of a nearby salad grower. Here it will act to accelerate the growth of tomatoes.
The partnership between Drax, FuelCell Energy, P3P Partners and the Department of Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy could provide an additional opportunity for the UK’s biggest renewable power generator to deploy bioenergy carbon capture usage and storage (BECCUS) at scale in the mid 2020s.
From powering space ships in the 70s to offering greenhouse-gas free transport, fuel cells continue to advance. As low-carbon electricity sources become more important they’re set to play a bigger role yet.
Learn more about carbon capture, usage and storage in our series:
- Planting, sinking, extracting – some of the ways to absorb carbon from the atmosphere
- From capture methods to storage and use across three continents, these companies are showing promising results for CCUS
- Why experts think bioenergy with carbon capture and storage will be an essential part of the energy system
- The science of safely and permanently putting carbon in the ground
- The numbers must add up to enable negative emissions in a zero carbon future, says Drax Group CEO Will Gardiner.
- The power industry is leading the charge in carbon capture and storage but where else could the technology make a difference to global emissions?
- A roadmap for the world’s first zero carbon industrial cluster: protecting and creating jobs, fighting climate change, competing on the world stage
- Can we tackle two global challenges with one solution: turning captured carbon into fish food?
- How algae, paper and cement could all have a role in a future of negative emissions
- How the UK can achieve net zero
- Transforming emissions from pollutants to products
- Drax CEO addresses Powering Past Coal Alliance event in Madrid, unveiling our ambition to play a major role in fighting the climate crisis by becoming the world’s first carbon negative company
The renewable pioneers

People love to celebrate inventors. It’s inventors that Apple’s famous 90s TV ad claimed ‘Think Different’, and in doing so set about changing the world. The renewable electricity sources we take for granted today all started with such people, who for one reason or another tried something new.
These are the stories of the people behind five sources of renewable electricity, whose inventions and ideas could help power the world towards a zero-carbon future.
The magician’s hydro house
Using rushing rivers as a source of power dates back centuries as a mechanised way of grinding grains for flour. The first reference to a watermill dates from all the way back to the third century BCE.
However, hydropower also played a big role in the early history of electricity generation – the first hydroelectric scheme first came into action in 1878, six years before the invention of the modern steam turbine.
What important device did this early source of emissions-free electricity power? A single lamp in the Northumberland home of Victorian inventor William Armstrong. This wasn’t the only feature that made the house ahead of its time.
Water pressure also helped power a hydraulic lift and a rotating spit in the kitchen, while the house also featured hot and cold running water and an early dishwasher. One contemporary visitor dubbed the house a ‘palace of a modern magician’.
The first commercial hydropower power plant, however, opened on Vulcan Street in Appleton, Wisconsin in 1882 to provide electricity to two local paper mills, as well as the mill owner H.J. Rogers’ home.
After a false start on 27 September, the Vulcan Street Plant kicked into life in earnest on 30 September, generating about 12.5 kilowatts (kW) of electricity. It was very nearly America’s first ever commercial power plant, but was beaten to the accolade by Thomas Edison’s Pearl Street Plant in New York which opened a little less than a month earlier.
The switch to silicon that made solar possible

When the International Space Station is in sunlight, about 60% the electricity its solar arrays generate is used to charge the station’s batteries. The batteries power the station when it is not in the sun.
For much of the 20thcentury solar photovoltaic power generation didn’t appear in many more places than on calculators and satellites. But now with more large-scale and roof-top arrays popping up, solar is expected to generate a significant portion of the world’s future energy.
It’s been a long journey for solar power from its origins back in 1839 when 19-year old aspiring physicist Edmond Becquerel first noticed the photovoltaic effect. The Frenchman found that shining light on an electrode submerged in a conductive solution created an electric current. He did not, however, have any explanation for why this happened.
American inventor Charles Fritts was the first to take solar seriously as a source of large-scale generation. He hoped to compete with Thomas Edison’s coal powered plants in 1883, when he made the first recognisable solar panel using the element selenium. However, they were only about 1% efficient and never deployed at scale.
It would not be until 1953, when scientists Calvin Fuller, Gerald Pearson and Daryl Chapin working at Bell Labs cracked the switch from selenium to silicon, that the modern solar panel was created.
Bell Labs unveiled the breakthrough invention to the world the following year, using it to power a small toy Ferris wheel and a radio transmitter.
Fuller, Pearson and Chapin’s solar panel was only 6% efficient, a big step forward for the time, but today panels can convert more than 40% of the sun’s light into electricity.
The wind pioneers who believed in self-generation

Offshore wind farm near Øresund Bridge between Sweden and Denmark
Like hydropower, wind has long been harnessed as a source of power, with the earliest examples of wind-powered grain mills and hydro pumps appearing in Persia as early as 500 BC.
The first electricity-generating windmill was used to power the mansion of Ohio-based inventor Charles Brush. The 60-foot (18.3 metres) wooden tower featured 144 blades and supplied about 12 kW of electricity to the house.
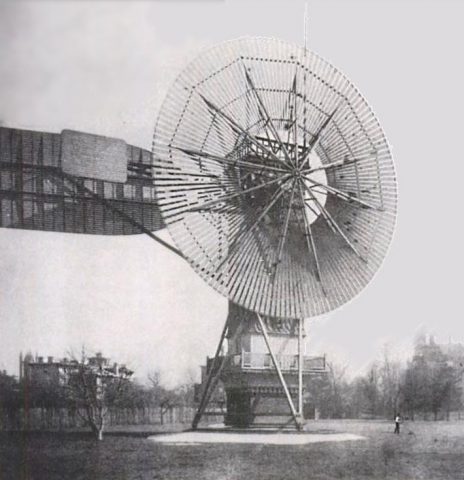

Charles Brush’s wind turbine charged a dozen batteries each with 34 cells.
The turbine was erected in 1888 and powered the house for two decades. Brush wasn’t just a wind power pioneer either, and in the basement of the mansion sat 12 batteries that could be recharged and act as electricity sources.
Small turbines generating between 5 kW and 25 kW were important at the turn of the 19thinto the 20thcentury in the US when they helped bring electricity to remote rural areas. However, over in Denmark, scientist and teacher Poul la Cour had his own, grander vision for wind power.
La Cour’s breakthroughs included using a regulator to maintain a steady stream of power, and discovering that a turbine with fewer blades spinning quickly is more efficient than one with many blades turning slowly.
He was also a strong advocate for what might now be recognised as decentralisation. He believed wind turbines provided an important social purpose in supplying small communities and farms with a cheap, dependable source of electricity, away from corporate influence.
In 2017, Denmark had more than 5.3 gigawatts (GW) of installed wind capacity, accounting for 44% of the country’s power generation.
The prince and the power plant

Larderello, Italy
Italian princes aren’t a regular sight in the history books of renewable energy, but at the turn of the last century, on a Tuscan hillside, Piero Ginori Conti, Prince of Trevignano, set about harnessing natural geysers to generate electricity.
In 1904 he had become head of a boric acid extraction firm founded by his wife’s great-grandfather. His plan for the business included improving the quality of products, increasing production and lowering prices. But to do this he needed a steady stream of cheap electricity.
In 1905 he harnessed the dry steam (which lacks moisture, preventing corrosion of turbine blades) from the geographically active area near Larderello in Southern Tuscany to drive a turbine and power five light bulbs. Encouraged by this, Conti expanded the operation into a prototype power plant capable of powering Larderello’s main industrial plants and residential buildings.
It evolved into the world’s first commercial geothermal power plant in 1913, supplying 250 kW of electricity to villages around the region. By the end of 1943 there was 132 megawatts (MW) of installed capacity in the area, but as the main source of electricity for central Italy’s entire rail network it was bombed heavily in World War Two.
Following reconstruction and expansion the region has grown to reach current capacity of more than 800 MW. Globally, there is now more than 83 GW of installed geothermal capacity.
The engineer who took on an oil crisis with wood

Compressed wood pellet storage domes at Baton Rouge Transit, Drax Biomass’ port facility on the Mississippi River
While sawmills had experimented with waste products as a power sources and compressed sawdust sold as domestic fuel, it wasn’t until the energy crisis of the 1970s that the term biomass was coined and wood pellets became a serious alternative to fossil fuels.
As a response to the 1973 Yom Kippur War, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) placed oil embargoes against several nations, including the UK and US. The result was a global price increase from $3 in October 1973 to $12 in March 1974, with prices even higher in the US, where the country’s dependence on imported fossil fuels was acutely exposed.
One of the most vulnerable sectors to booms in oil prices was the aviation industry. To tackle the growing scarcity of petroleum-based fuels, Boeing looked to fuel-efficiency engineer Jerry Whitfield. His task was to find an alternative fuel for industries such as manufacturing, which were hit particularly hard by the oil shortage and subsequent recession. This would, in turn, leave more oil for planes.

Wood pellets from Morehouse BioEnergy, a Drax Biomass pellet plant in northern Louisiana, being unloaded at Baton Rouge Transit for storage and onward travel by ship to England.
Whitfield teamed up with Ken Tucker, who – inspired by pelletised animal feed – was experimenting with fuel pellets for industrial furnaces. The pelletisation approach, combined with Whitfield’s knowledge of forced-air furnace technology, opened a market beyond just industrial power sources, and Whitfield eventually left Boeing to focus on domestic heating stoves and pellet production.
One of the lasting effects of the oil crisis was a realisation in many western countries of the need to diversify electricity generation, prompting expansion of renewable sources and experiments with biomass cofiring. Since then biomass pellet technology has built on its legacy as an abundant source of low-carbon, renewable energy, with large-scale pellet production beginning in Sweden in 1992. Production has continued to grow as more countries decarbonise electricity generation and move away from fossil fuels.
Since those original pioneers first harnessed earth’s renewable sources for electricity generation, the cost of doing so has dropped dramatically and efficiency skyrocketed. The challenge now is in implementing the capacity and technology to build a safe, stable and low-carbon electricity system.
What causes power cuts?

On the night of 5 December 2015, 61,000 homes and properties across Lancaster were plunged into darkness. Storm Desmond had unleashed torrents of rain on Great Britain, causing rivers to swell and spill over. With waters rising to unprecedented levels, the River Lune began threatening to flood Lancaster’s main electricity substation, the facility where transformers ‘step down’ electricity’s voltage from the transmission system so it can be distributed safely around the local area.
To prevent unrepairable damage, the decision was taken to switch the substation off, cutting all power across the region. Lights, phones, internet connections and ATMs all went dead across the city. It would take three days of intensive work before power was restored.
It was a bigger power outage than most, but it offers a unique glimpse into the mechanisms behind a blackout – not only how they’re dealt with, but how they’re caused.
What causes blackouts in Great Britain?
When the lights go out, a common thought is that the country has ‘run out’ of electricity. However, a lack of electricity generation is almost never the cause of outages. Only during the miners’ strikes of 1972 were major power cuts the result of lack of electricity production.
Rather than meeting electricity demand, power cuts in Great Britain are more often the result of disruption to the transmission system, caused by unpredictable weather. If trees or piles of snow bring down one power line, the load of electric current shifts to other lines. If this sudden jump in load is too much for the other lines they automatically trip offline to prevent damage to the equipment. This in turn shifts the load on to other lines which also then trip, potentially causing cascading outages across the network.
Last March’s ‘Beast from the East’, which brought six days of near sub-zero temperatures, deep snow and high winds to Great Britain, is an example of extreme weather cutting electricity to as many as 18,000 people.
High-winds brought trees and branches down onto powerlines, while ice and snow impacted the millions of components that make up the electricity system. Engineering teams had to fight the elements and make the repairs needed to get electricity flowing again.
Lancaster was different, however. With the slow creep of rising rainwater approaching the substation, the threat of long lasting damage was plain to see in advance, and so rather than waiting for it to auto-trip, authorities chose to manually shut it down.
Getting reconnected
Electricity North West is Lancaster’s network operator and after shutting down the substation, it began the intensive job of trying to restore power. On Monday 7 December, two days after the storm hit, the first step of pumping the flooded substation empty of water had finally been completed and the task of reconnecting it began.
To begin restoring power to the region 75 large mobile generators were brought from as far away as the West Country and Northern Ireland and hooked up to the substation, allowing 22,000 customers to be reconnected.
Once partial power was restored, the next challenge lay in repairing and reconnecting the substation to the transmission network. While shutting the facility had prevented catastrophic damage, some of the crucial pieces had to be completely replaced or rebuilt. After three days of intensive engineering work the remaining 40,000 properties that had lost power were reconnected.
Preventing blackouts in a changing system

The cause and scale of Lancaster’s outage were unusual for Great Britain’s electricity system but it does highlight how quickly a power cut may arise. In a time of transition, when the grid is decarbonising and the network is facing more extreme weather conditions because of climate change, it could create even more, new challenges.
Coal is scheduled to be taken entirely off the system after 2025, making the country more reliant on weather-dependent sources, such as wind and solar – potentially increasing the volatility of the system.
On the other hand, growing decentralised electricity generation may reduce the number of individual buildings affected by outages in the future. Solar generation and storage systems present on domestic and commercial property may also reduce dependency on local transmission systems and the impact of disruptions to it.
The cables and poles that connect the transmission system will always be vulnerable to faults and disruptions. However, by preparing for the future grid Great Britain can reduce the impact of storms on the electricity system.




