- Drax and MOL Drybulk partner to develop wind power technology that will reduce biomass shipping emissions by a fifth
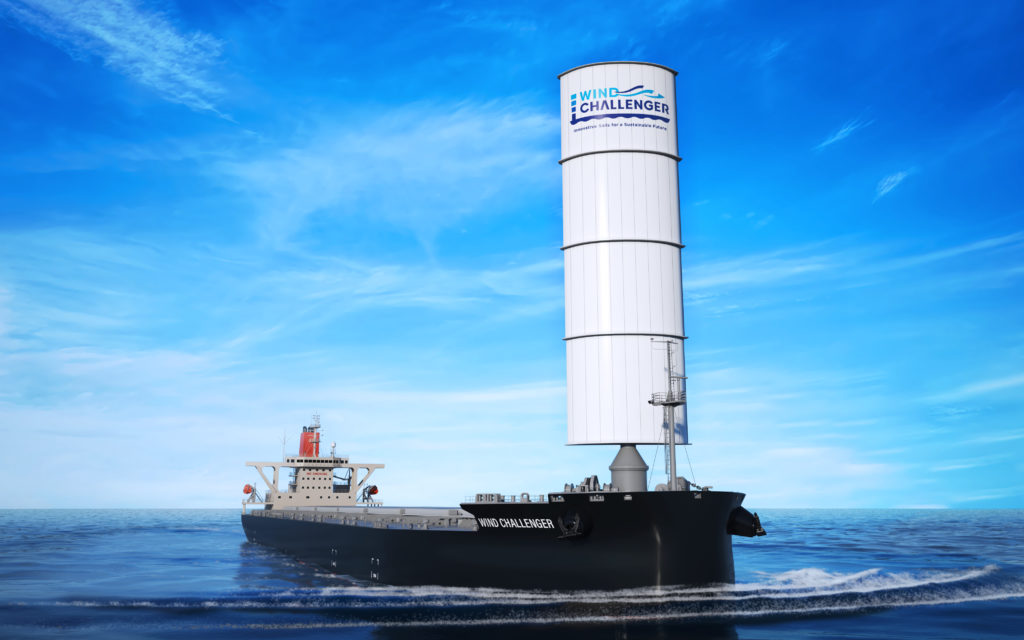
- Newly built vessels will be fitted with MOL’s Wind Challenger hard sail technology, with first ship expected as soon as 2025
- The initiative is part of Drax’s plans to reduce its supply chain emissions and become carbon negative by 2030 using bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS)
The companies plan to facilitate the development of wind-powered vessels to transport bulk cargoes of Drax’s wood pellets to its customers in Japan, where the biomass is used to generate reliable, renewable energy, which displaces fossil fuels.
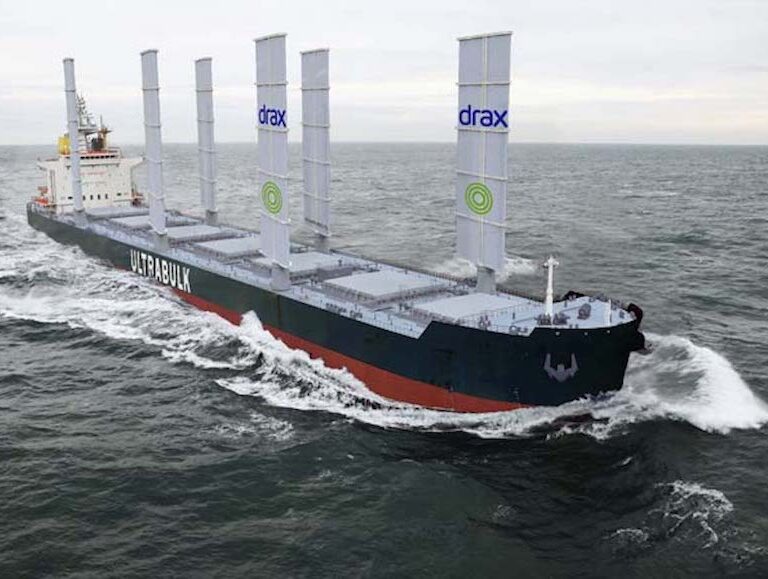
EFBC-1 (Wind Challenger and Rotor sails)
The newly built vessels will be fitted with MOL’s Wind Challenger hard sail technology, with the first ship expected to be on the water as soon as 2025.
The initiative is part of Drax’s plans to further reduce supply chain emissions in line with its world-leading ambition to be a carbon negative company by 2030, by using bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS).
Drax Group Chief Executive Will Gardiner said:
Drax Group CEO Will Gardiner
“MOL Drybulk’s hard sail technology has the potential to transform the maritime industry, cutting emissions and fuel costs and supporting global efforts to address the climate crisis.
“This partnership to advance this crucial new technology will support Drax’s commitment to reduce its own supply chain emissions and could also deliver far-reaching benefits across a number of different sectors that rely on ships to carry goods to customers around the world.”
Under the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), the two companies will study the feasibility of deploying a first and second generation Environmentally Friendly Bulk Carrier (EFBC) to carry Drax’s biomass.
The first EFBC will use MOL’s automated telescopic hard sail technology – Wind Challenger, and will evaluate the application of other technologies including rotor sails.
The second EFBC aims to at least halve emissions with new vessel designs that use multiple Wind Challenger sails, other low-carbon technologies in development and the use of alternative fuels such as ammonia, liquefied natural gas and synthetic fuels.
- Sail from the rear – extended
- Sail from the rear – retracted
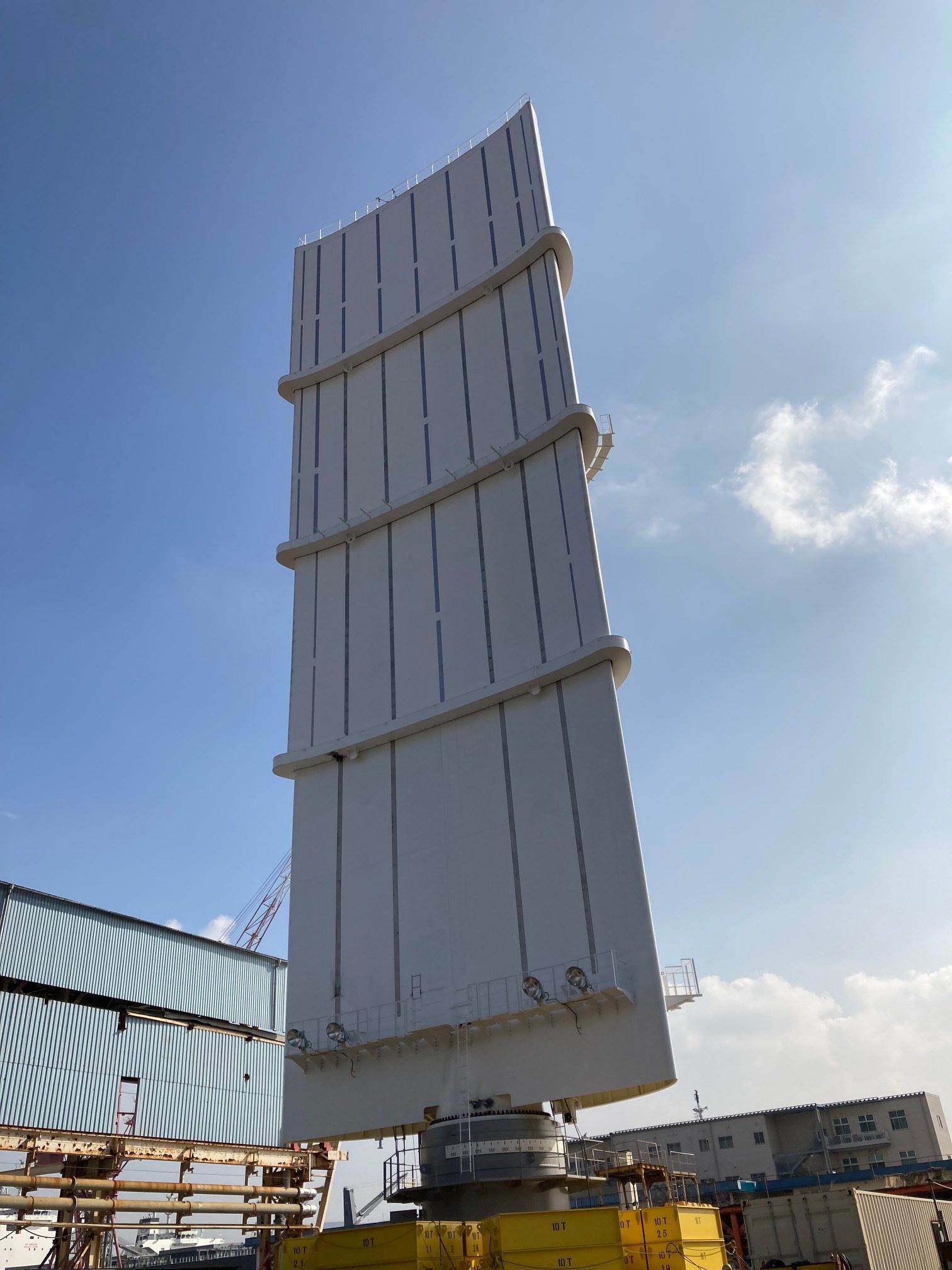
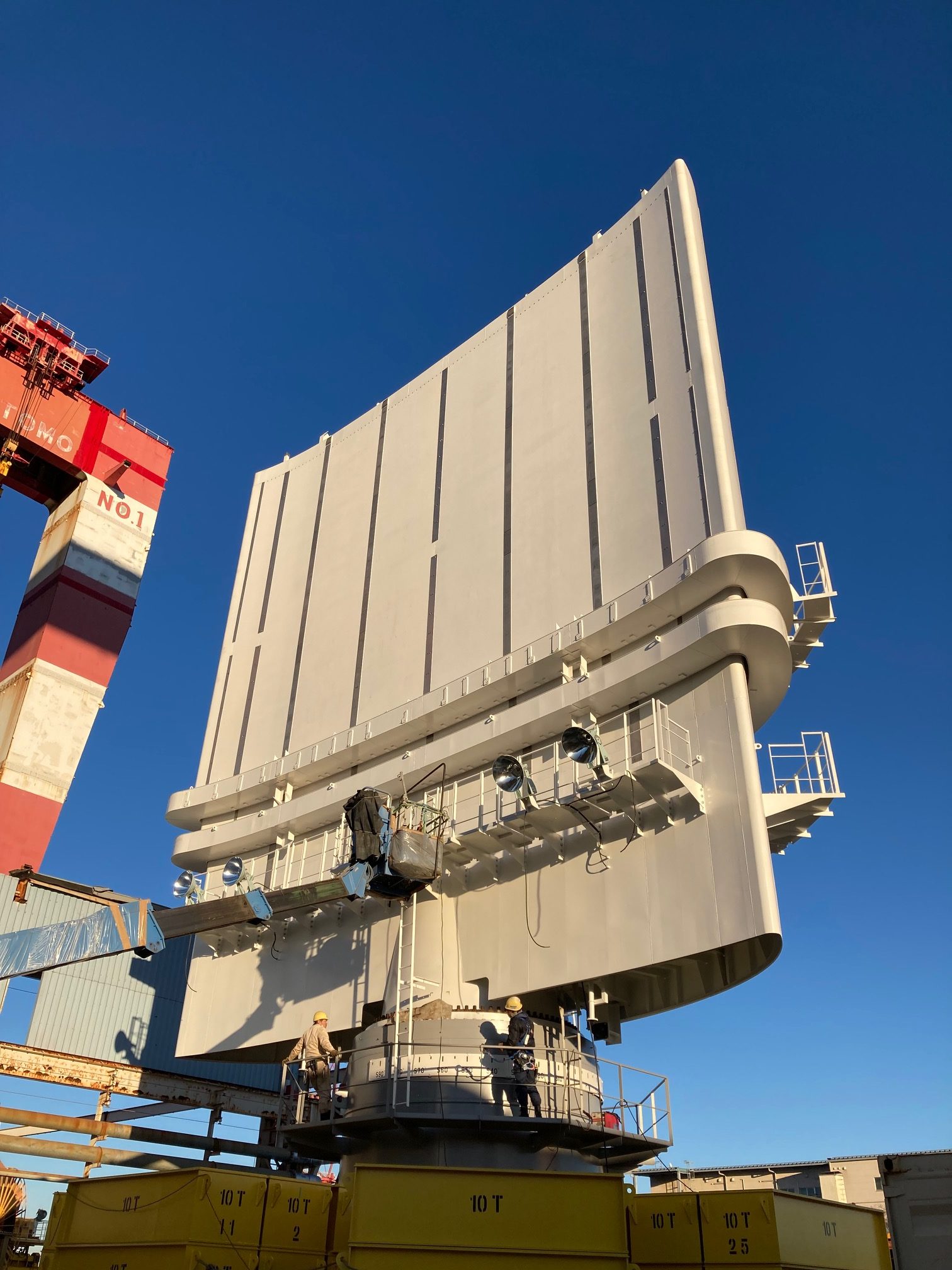
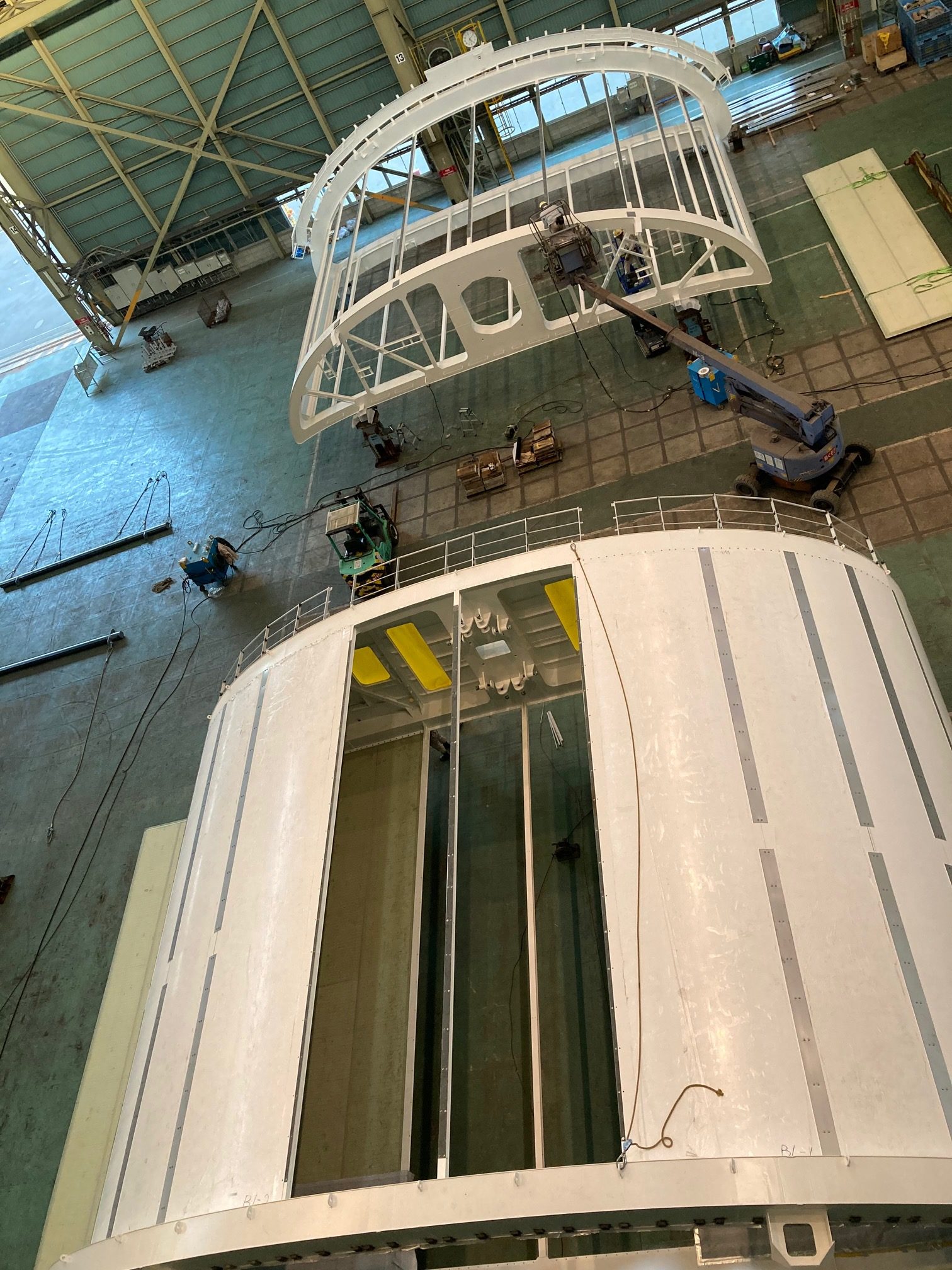
- Construction of the Wind Challenger sail at Oshima Shipbuilding Yard
Kazuhiko Kikuchi, President and Representative Director of MOL Drybulk said:
Kazuhiko Kikuchi, President and Representative Director of MOL Drybulk
“MOL has been working with our partners to develop the Wind Challenger technology for over a decade, and it’s great to see this become a reality.”
“We are extremely excited to work together with an innovative company such as Drax. This partnership will help us have a positive impact on how wood pellets and other cargoes are transported across the world.”
MOL Drybulk’s work will include developing the technologies that will be used and liaising with the shipyard where the vessel will be built and fitted with the hard sail technology. Drax will work with the ports and terminals in the supply chain on the operational feasibility studies.
The MoU with MOL Drybulk follows Drax’s previous work with the Smart Green Shipping Alliance to look at the potential of fitting innovative sail technology on ships transporting biomass from the US to the UK.
ENDS
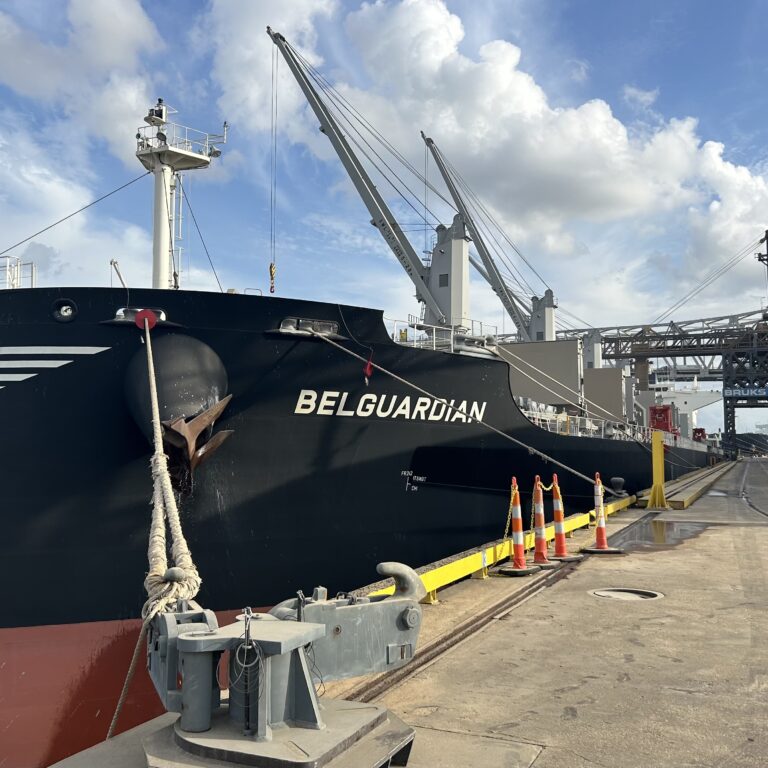
Top image caption: Image of the vessel fitted with Wind Challenger technology that will be launched later this year
Video: https://youtu.be/yXbvG6VrwNc
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TzMY2FFogzQ
Media contacts:
Selina Williams
Drax Media Manager
E: selina.williams@drax.com
T: +44 (0)7912 230 393
MOL Drybulk
ICT Communication Team
E: DBICT@molgroup.com
Editor’s Notes
- International shipping is the backbone of the global economy, transporting about 90% of global trade volumes. The sector produces around 940 million tonnes of CO2 a year – around 2.5% of the world’s total CO2
- Drax has already cut emissions from its fossil fuel generation by over 95% since 2012 and is targeting further reductions for its remaining emissions, including in its supply chain.
- Drax reports its supply chain emissions in its Annual Report, which is independently audited.
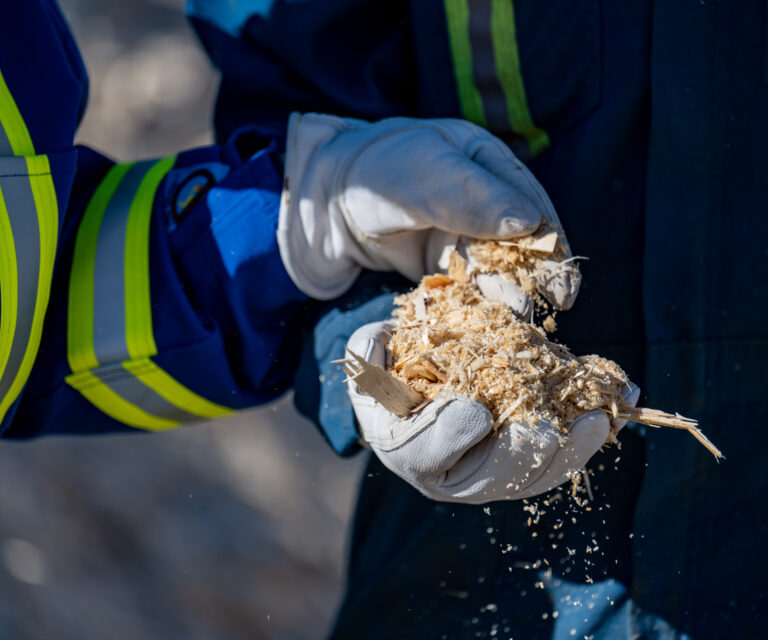
- Drax’s biomass comes from sustainably managed working forests. It includes the residuals left behind after harvesting activities for other sectors such as construction and furniture, as well as sawmill residues and thinnings.
- MOL Drybulk is a 100% subsidiary of Mitsui O.S.K. Lines Ltd. (MOL)
- MOL has set out its plans to reach net zero by 2050
About Drax
Drax Group’s purpose is to enable a zero carbon, lower cost energy future and in 2019 announced a world-leading ambition to be carbon negative by 2030, using Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) technology.
Drax’s around 3,000 employees operate across three principal areas of activity – electricity generation, electricity sales to business customers and compressed wood pellet production and supply to third parties. For more information visit www.drax.com
Power generation:
Drax owns and operates a portfolio of renewable electricity generation assets in England and Scotland. The assets include the UK’s largest power station, based at Selby, North Yorkshire, which supplies five percent of the country’s electricity needs.
Having converted Drax Power Station to use sustainable biomass instead of coal it has become the UK’s biggest renewable power generator and the largest decarbonisation project in Europe. It is also where Drax is piloting the groundbreaking negative emissions technology BECCS within its CCUS (Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage) Incubation Area.
Its pumped storage, hydro and energy from waste assets in Scotland include Cruachan Power Station – a flexible pumped storage facility within the hollowed-out mountain Ben Cruachan.
The Group also aims to build on its BECCS innovation at Drax Power Station with a target to deliver 4Mt of negative CO2 emissions each year from new-build BECCS outside of the UK by 2030 and is currently developing models for North American and European markets.
Pellet production and supply:
The Group has 17 operational pellet plants and developments with nameplate production capacity of around 5 million tonnes a year once developments are complete.
Drax is targeting 8Mt of production capacity by 2030, which will require the development of over 3Mt of new biomass pellet production capacity. The pellets are produced using materials sourced from sustainably managed working forests and are supplied to third party customers in Europe and Asia for the generation of renewable power.
Drax’s pellet plants supply biomass used at its own power station in North Yorkshire, England to generate flexible, renewable power for the UK’s homes and businesses and also to customers in Europe and Asia.
Customers:
Drax supplies renewable electricity to UK businesses, offering a range of energy-related services including energy optimisation, as well as electric vehicle strategy and management.
To find out more go to the website www.energy.drax.com
About MOL Drybulk
MOL Drybulk Ltd. is a 100% Subsidiary company of Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, and is a unique entity operating vessels ranging from 10,000DWT up to 100,000DWT bulk carriers, wood chip carriers and multi-purpose vessels, with the aim to provide a “one-stop service” to the customers, work collaboratively to meet their needs and provide environmental solutions to reduce the GHG emissions throughout the supply chain.
About Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. (MOL)
Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. (MOL), as a global marine transport group, operates a global fleet exceeding 700 vessels, including tankers, bulkers, car carriers, ferries, which also extends to offshore projects. Under the “MOLGROUP Environmental Vision 2.1” established in June 2021, MOL clarifies its commitment to achieve sustainable “Net Zero GHG Emissions” by 2050 through collective efforts with all capabilities within the group.
The “Wind Challenger”
The Wind Challenger Project started in 2009 with the “Wind Challenger Plan,” an industry-academia joint research project led by The University of Tokyo, and in January 2018, MOL and Oshima Shipbuilding took charge of the plan and now play a central role in this project. The system converts wind energy to propulsive force with a telescopic hard sail.
In October 2019, it acquired Approval in Principle (AIP) for the design of a hard sail system.
In December 2020, MOL reached a long-term transport deal with Tohoku Electric Power Co., Inc. using a 99,000DWT vessel equipped with a Wind Challenger sail with the aim to achieve 5% to 8% reduction of the GHG emissions. The vessel is currently constructed at Oshima Shipbuilding, and is scheduled to commence service in Q4 2022.
YouTube





















