Tony Juniper* is an environmental campaigner, author and director at Robertsbridge, a consultancy helping advise Drax on its sustainability programmes
Back in 2006 while working as Director at Friends of the Earth I approved a new report to be published in support of our then campaign for a new Climate Change Act. We wanted to show UK government ministers how it would indeed be possible to make cuts in emissions so that by 2050 the UK could progressively have reduced greenhouse gas pollution by 80 per cent compared with emissions in 1990. It was a radical and demanding agenda that we’d adopted and it was important to show the practical steps that could be made in achieving it.
The analysis we presented was based on an electricity sector model that we had developed. Different data and assumptions could be inputted and using this we set out six possible lower carbon futures.
In our best case scenario we foresaw how it would be feasible to slash emissions by about 70 per cent by 2030.
This was based on an ambitious energy efficiency programme and a shift away from fossil energy and toward renewables, including wind and solar power. In that renewables mix was also an important role for biomass to replace coal in the country’s largest power station – Drax.

This was not only crucial for backing up intermittent renewable sources but also a key piece in a future electricity sector that we believed should avoid the construction of new nuclear power stations. In November 2008 our campaign succeeded and the UK was the first country in the world to adopt a new national law for the science-based reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Since then I’ve been working as an independent sustainability advisor, including with the advisory group Robertsbridge, of which I was a co-founder.
My work has included assisting various companies in meeting the targets set out in that new law. For example, I was the Chair of the industry campaign Action for Renewables which sought government and public support for the large-scale expansion of wind, tidal and wave power.
Different campaigners tried to stop the expansion of these renewable sources of electricity, however, and succeeded in derailing support for on-shore wind power developments.
Although in its infancy, concerns were also raised about proposals for different kinds of tidal power.
In the years after the Climate Change Act I was encouraged to see that Drax began to switch over to wood pellets to generate power but concerned to see that this too had come under attack. The broadly agreed view that sustainable biomass could have a role in the phase out of coal had gone, and in its place were claims that it was actually worse than burning coal. It was against this backdrop of changed perspectives that myself and Robertsbridge colleagues were pleased to be invited to help Drax in devising a new sustainability plan.
Early on in our conversations with Drax it became clear that part of the challenge with biomass — deciding the extent to which it is a rational choice to help with the process of decarbonisation, is how the answer to that touches so many different issues.
For example, when it comes to the exit from coal, cleaner alternatives must be brought forward to replace it, including wind and solar power.
But although these sources of renewable energy are growing rapidly, they still come with their own challenges, especially because wind can’t generate on still days and solar ceases at night. This intermittency raises issues about what the best electricity storage or complementary clean power sources might be to back them up when needed.
There are important questions about the best sources of biomass and the extent to which long-distance transport of that fuel is desirable. On top of that are issues linked with the management of the forests from which the raw material is sourced, and whether the extraction of wood to generate power can be compatible with carbon neutrality. There is the matter of nature conservation and the extent to which wood fuel demand will affect the status of species and habitats of conservation concern. For example, to what extent might the wood pellet industry be driving the conversion of semi-natural woodlands to plantations?

All of this is bound up with the economic and social conditions prevailing in the landscapes from which the wood is derived and the extent to which those buying wood fuel can pursue positive outcomes for the environment, even when carbon and wildlife are at best of marginal concern to the local forest owners growing the wood.
Then there is the extent to which economic incentives might be linked with the carbon stocks held in the forest. For example, strong demand for wood is held to be the main reason why since the 1950s the volume of carbon stored in standing timber in the forests of the US South has increased by over 100%.
Demand for wood might seem counter-intuitive as a positive factor in maintaining tree cover, but in the US South it has been a big part of the picture.

On top of all this is the question of what would happen if there were no demand for wood fuel. In landscapes that have seen volatility in demand arising from the decline in newsprint in favour of digital devices and the slowdown in US house building following the 2008 financial crisis, this is not easy to answer.
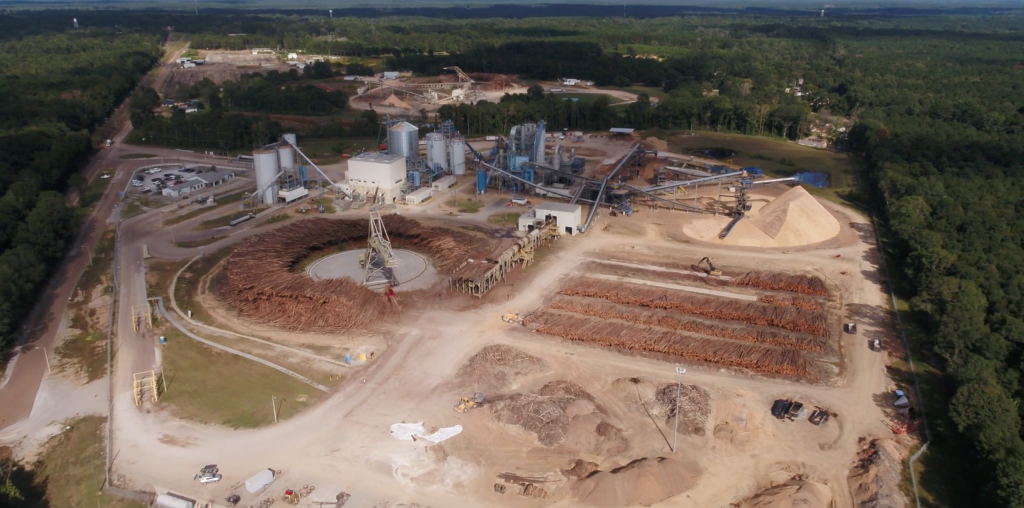

Although seeking answers is a complex task, our advice to Drax was that it should work with its many stakeholders in finding the best possible fit between its business planning and these and other questions.
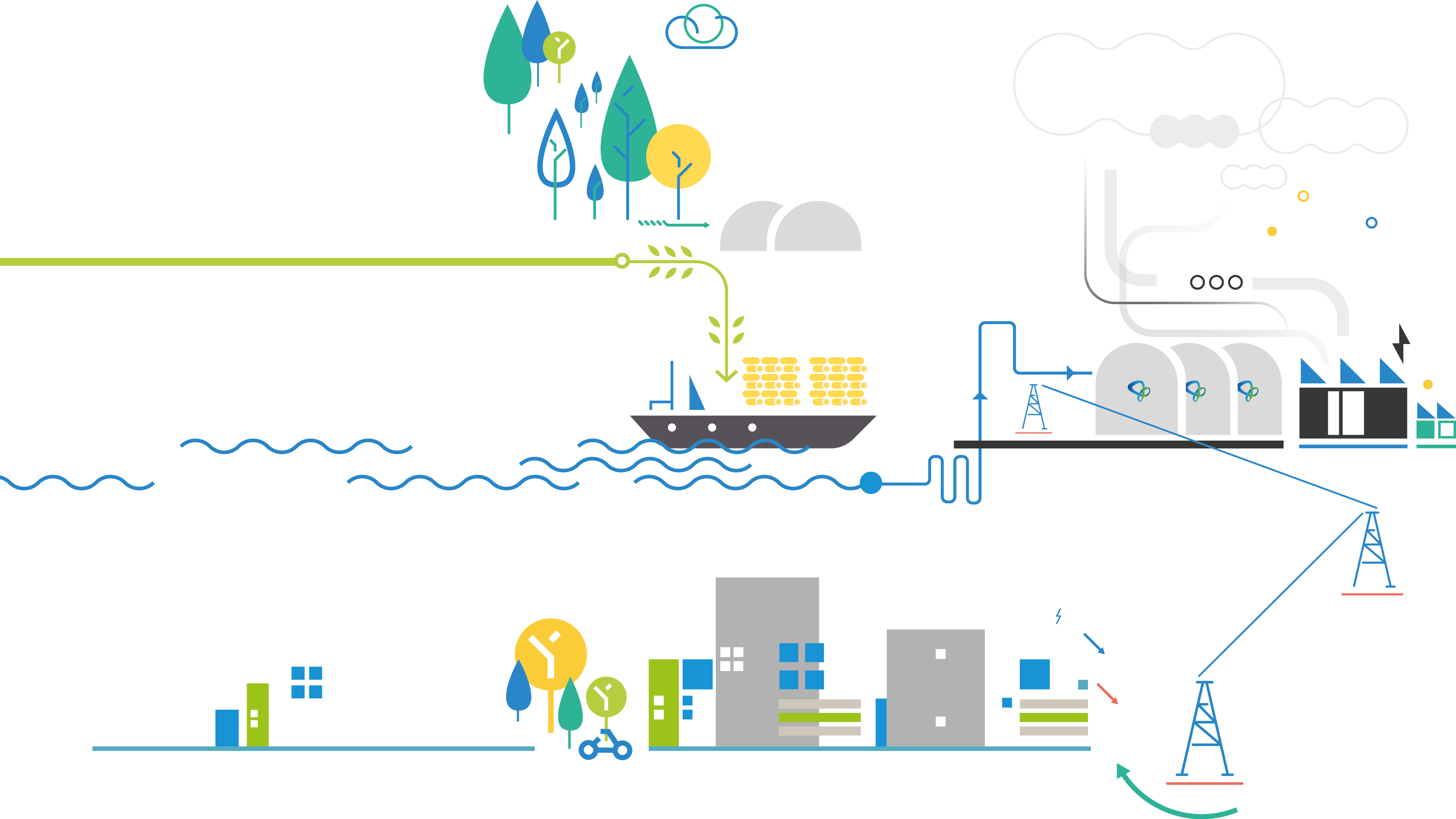
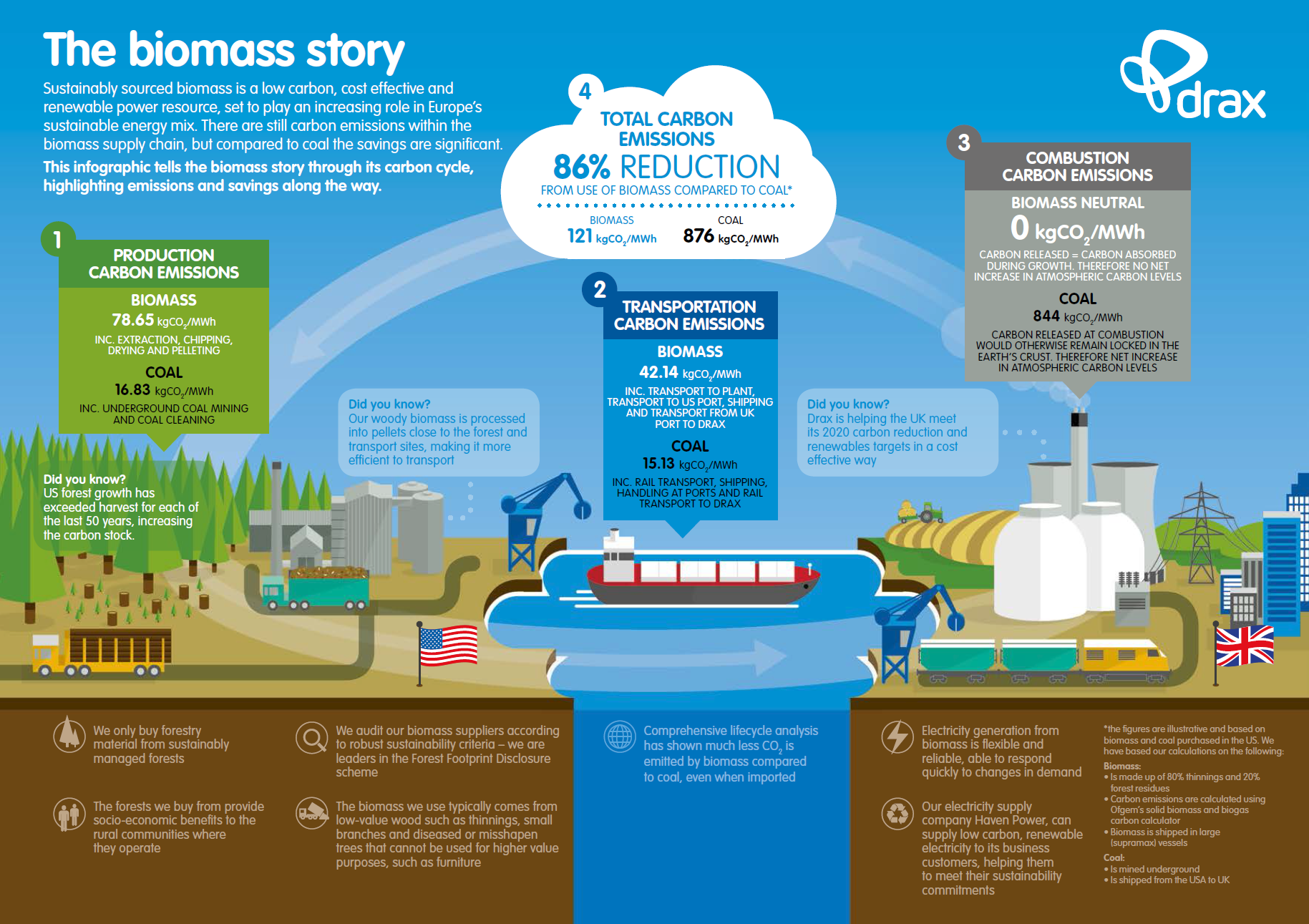
One way of doing that would be to set out the different issues in an accessible manner and hence the production of the film that can be seen here.
It’s called ‘The biomass sustainability story’ And while most of us can agree with the basic idea that we have to stop burning coal, it seems the big questions are about what might be the best ways to do it? Might biomass have a role? I believe it does.