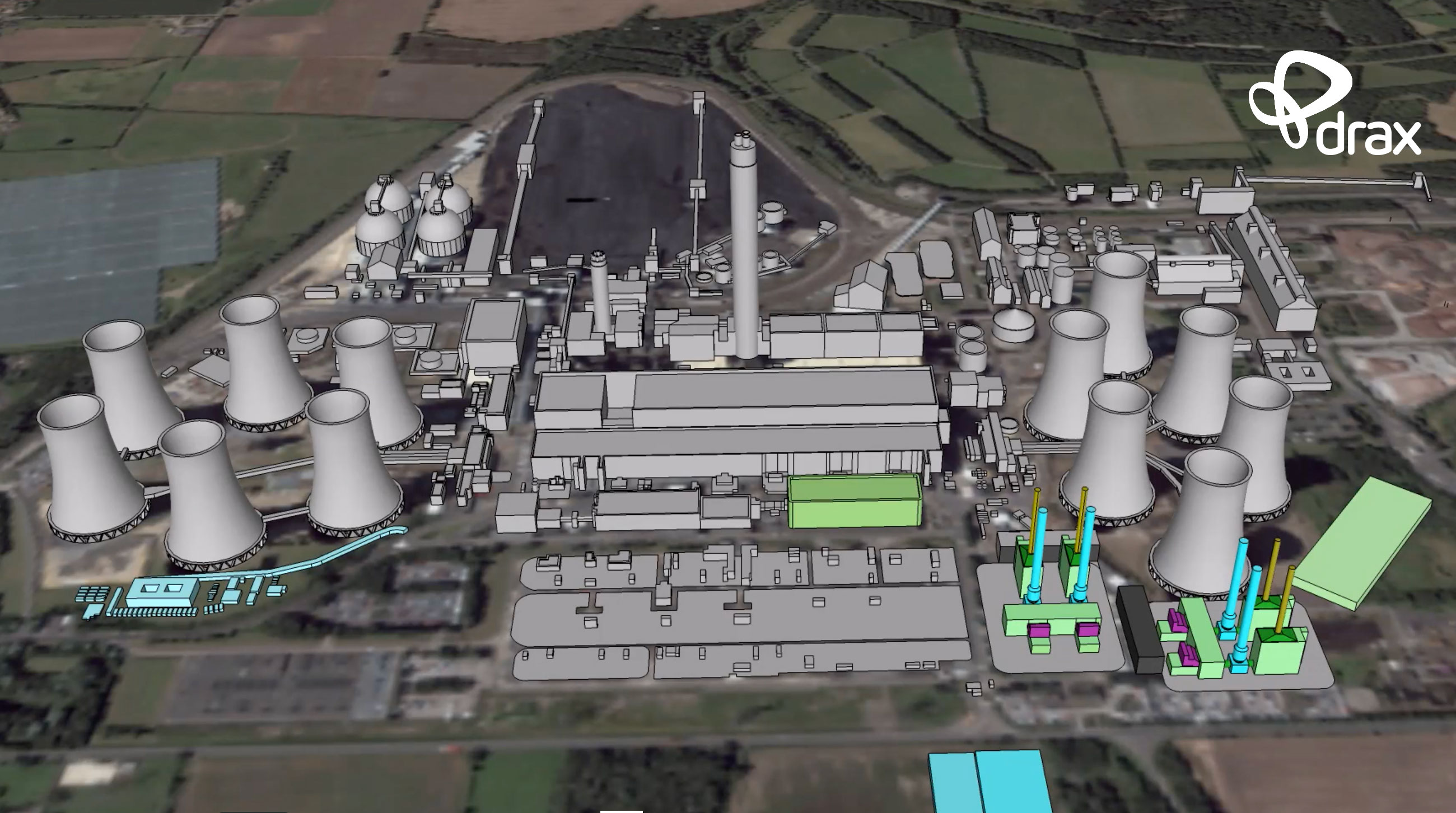
Drax has announced that it is to pilot the first bioenergy carbon capture storage (BECCS) project of its kind in Europe, which, if successful, could make the renewable electricity produced at its North Yorkshire power station carbon negative.
BECCS is vital to global efforts to combat climate change because the technology will mean the gases that cause global warning can be removed from the atmosphere at the same time as electricity is produced. This means power generation would no longer contribute to climate change, but would start to reduce the carbon accumulating in the atmosphere.
The demonstration project will see Drax partner with Leeds-based C-Capture and invest £400,000 in what could be the first of several pilot projects undertaken at Drax to deliver a rapid, lower cost demonstration of BECCS.
Drax Power Station became the largest decarbonisation project in Europe by upgrading its existing facilities and, if the pilot is successful, it will examine options for a similar re-purposing of existing infrastructure to deliver more carbon savings.
A report by the Energy Technology Institute in 2016 has suggested that by the 2050s BECCS could deliver roughly 55 million tonnes of net negative emissions a year in the UK – approximately half the nation’s emissions target.
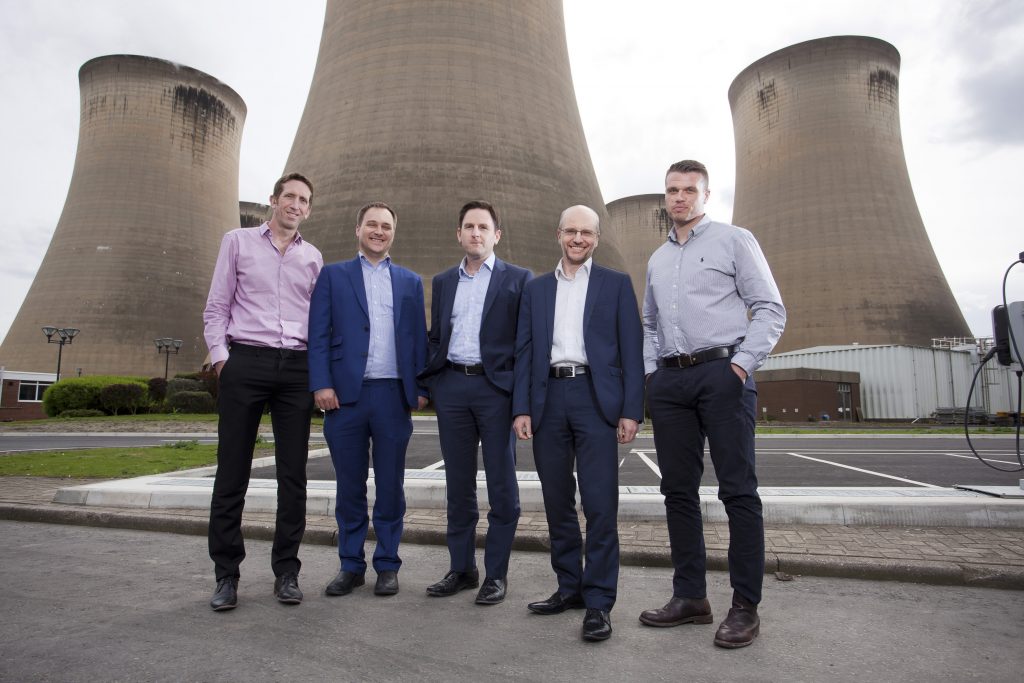

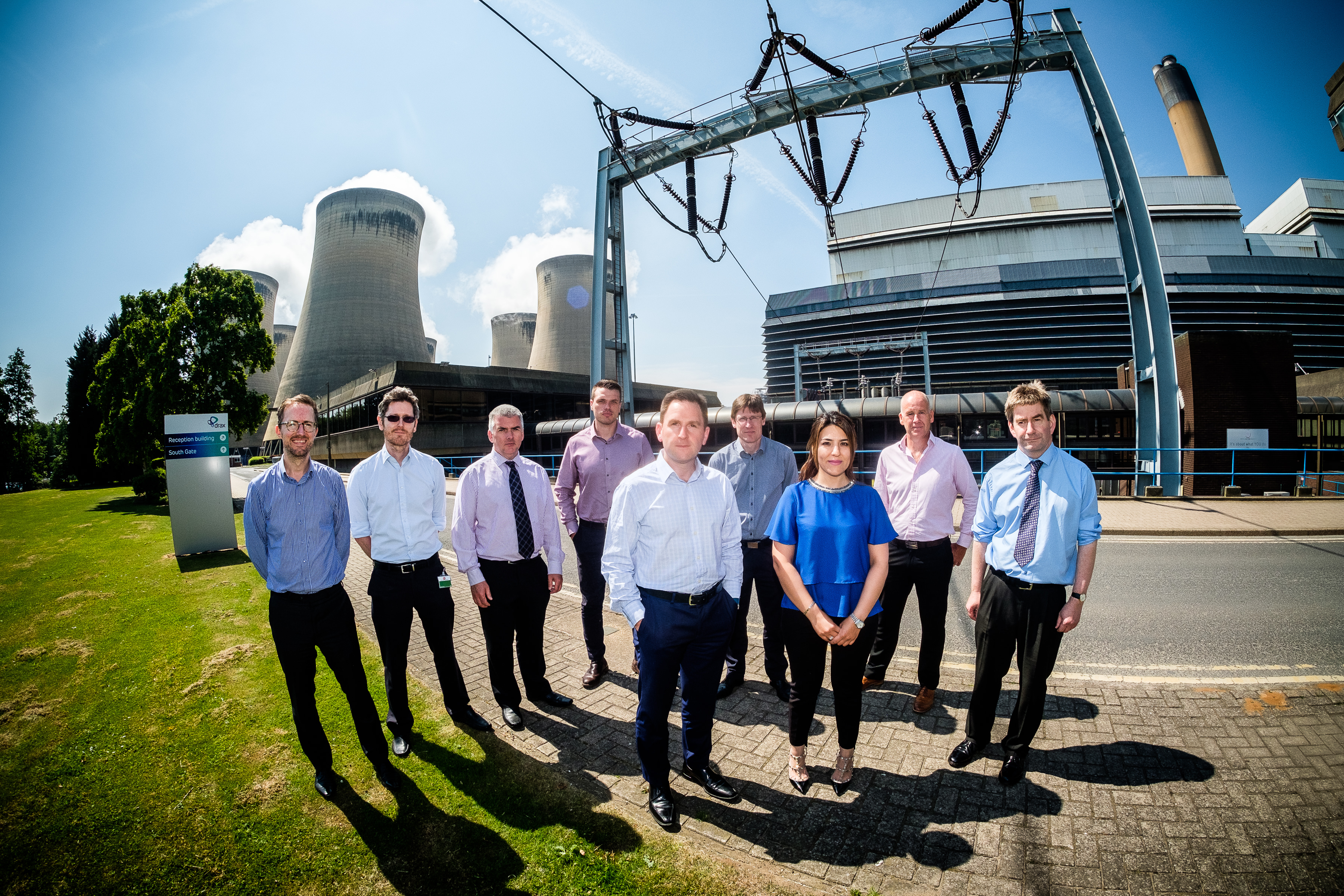
L-R: Jason Shipstone, Head of R&D, Drax Group; Caspar Schoolderman, Director of Engineering, C-Capture Ltd; Andy Koss, CEO Drax Power; Prof Christopher Rayner, Technical Director, C-Capture Ltd; Carl Clayton, Research and Innovation Engineer, Drax Group. Download high res photo.
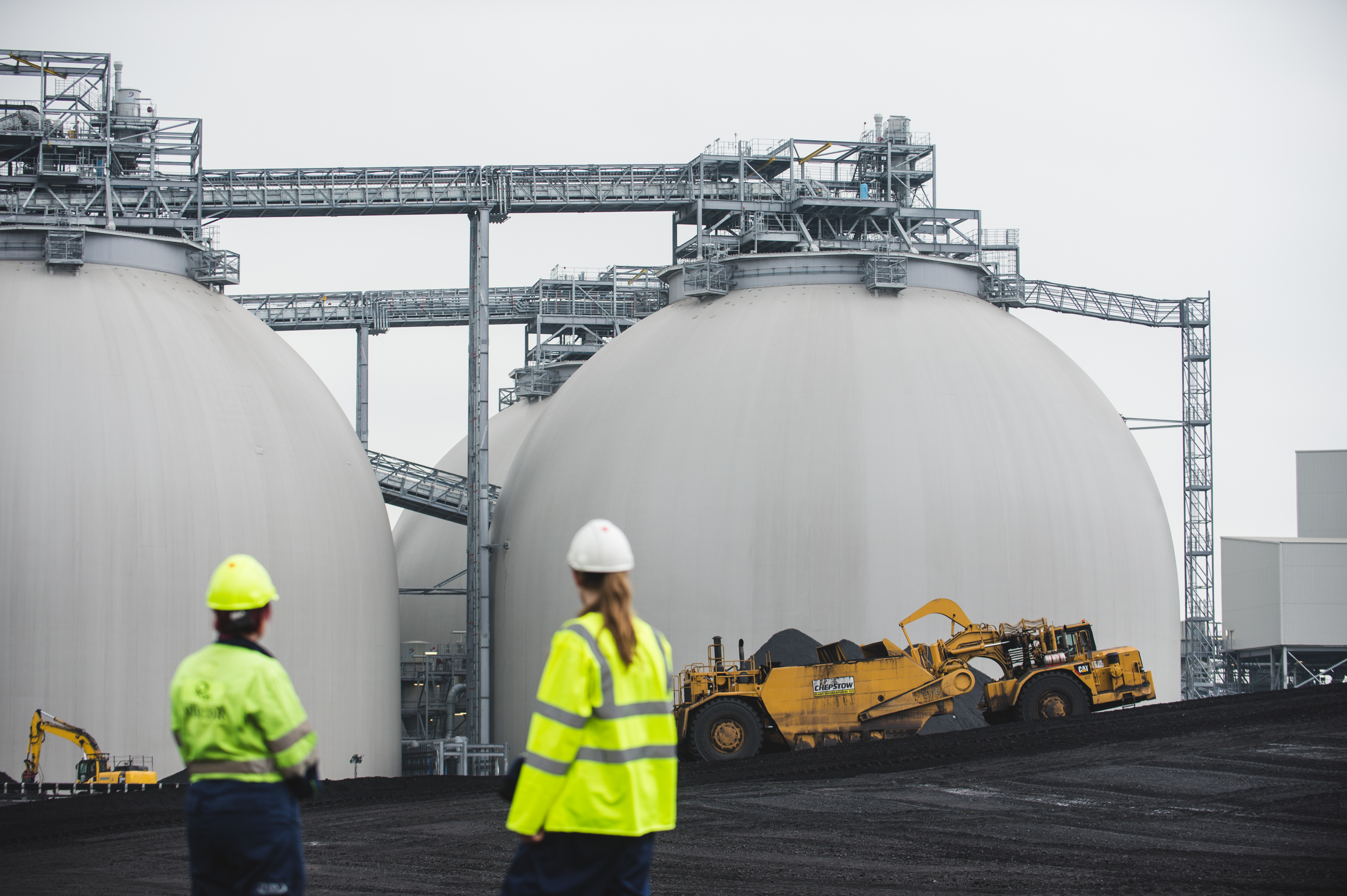
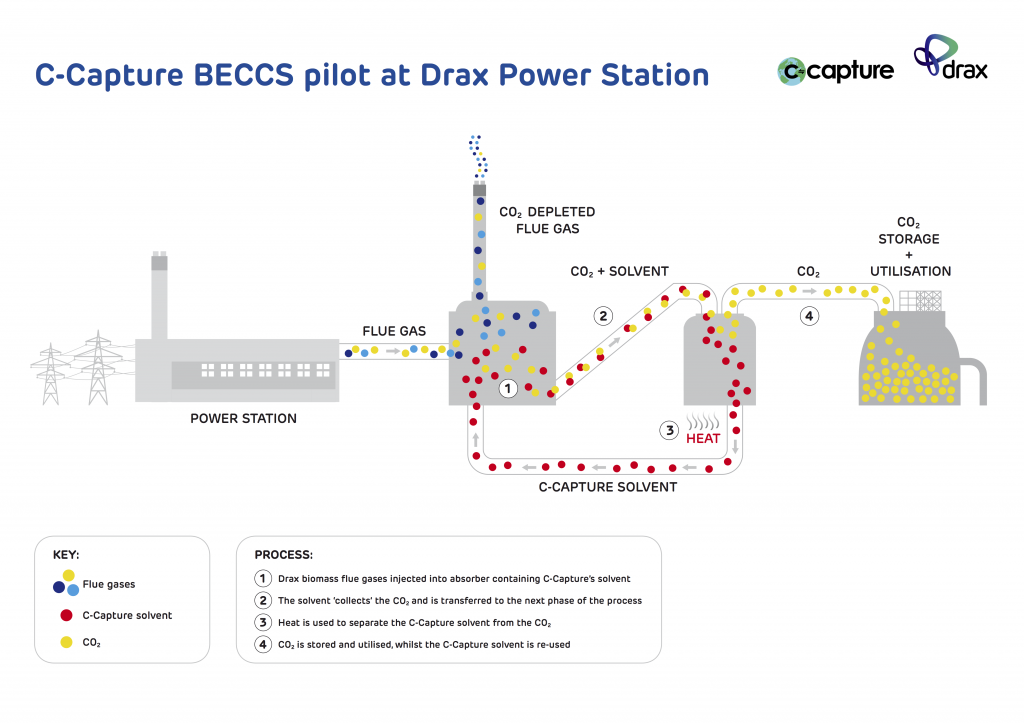
The first phase of the project, starting this month, will look to see if the solvent C-Capture has developed is compatible with the biomass flue gas at Drax Power Station. A lab-scale study into the feasibility of re-utilising the flue gas desulphurisation (FGD) absorbers at the power station will also be carried out to assess potential capture rates.
FGD equipment is vital for reducing sulphur emissions from coal, but has become redundant on three of the generating units at Drax that have been upgraded to use biomass, because the wood pellets used produce minimal levels of sulphur.
Depending on the outcome of a feasibility study, the C-Capture team will proceed to the second phase of the pilot in the autumn, when a demonstration unit will be installed to isolate the carbon dioxide produced by the biomass combustion.
Will Gardiner, CEO, Drax Group, said:
“If the world is to achieve the targets agreed in Paris and pursue a cleaner future, negative emissions are a must – and BECCS is a leading technology to help achieve it.
“This pilot is the UK’s first step, but it won’t be the only one at Drax. We will soon have four operational biomass units, which provide us with a great opportunity to test different technologies that could allow Drax, the country and the world, to deliver negative emissions and start to reduce the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.”
Unlike previous CCS projects Drax has been involved with, this is an early pilot for a new technology. It will examine the potential of a new form of carbon capture, post combustion on biomass, rather than coal.
The government’s Clean Growth Strategy identified BECCS as one of several greenhouse gas removal technologies that could remove emissions from the atmosphere and help achieve long term decarbonisation.
Claire Perry, Energy & Clean Growth Minister, said:
“We aim to make the UK a world leader in carbon capture usage and storage, a key part of our modern Industrial Strategy. It’s hugely exciting that Drax has chosen to invest in this innovative project, demonstrating how government support for innovation can create an environment where companies can develop new technologies and scale up investment to build the sectors we will need to achieve long term decarbonisation.”
C-Capture is a spin-out from the Department of Chemistry at the University of Leeds, established through funding from IP Group Plc.
Chris Rayner, founder of C-Capture and Professor of Organic Chemistry at the University of Leeds, said:
“We have developed fundamentally new chemistry to capture CO2 and have shown that it should be suitable for capturing the carbon produced from bioenergy processes.
“The key part is now to move it from our own facilities and into the real world at Drax. Through the pilot scheme we aim to demonstrate that the technology we’ve developed is a cost-effective way to achieve one of the holy grails of CO2 emissions strategies – negative emissions in power production, which is where we believe the potential CO2 emissions reductions are likely to be the greatest.”
Andy Duley, Director of Commercialisation at the University of Leeds, said:
“The University has an established track record in working with private sector investors and leveraging its own funds to launch successful spin out companies. C-Capture is the latest example of our continued success in converting research expertise into a valuable service which directly benefits industry, and has the potential to make an impact around the world.”
ENDS
Media contacts
Animation:
vimeo.com/draxgroup/beccs
Editor’s Notes
- Drax Power Station is the single largest user of sustainable biomass for power in the world – 65% of the electricity it produced in 2017 was renewable, enough to power four million households.
- Biomass, such as sustainably sourced compressed wood pellets, is a renewable fuel – the CO2 captured when it grew is equal to the emissions it releases when used to generate electricity so it does not contribute new carbon to the biosphere. When coupled with CCS, the overall process of biomass electricity generation removes more CO2 from the atmosphere than it releases.
- The government’s Clean Growth Strategy identified ‘sustainable biomass power stations used in tandem with CCUS technology’ as a potential route to achieving long-term decarbonisation between now and 2050.
- C-Capture is a spin out from the Chemistry Department at Leeds University and has attracted support from IP Group, the Department for Business Energy and Industrial Strategy’s Energy Entrepreneurs Fund and the CO2 Capture Project for CO2 capture technology, which has potential in a range of areas including biogas upgrading, natural gas sweetening and hydrogen production.
About Drax
Drax Group plc plays a vital role in helping change the way energy is generated, supplied and used. Its 2,300-strong staff operate across three principal areas of activity – electricity generation, electricity sales to business customers and compressed wood pellet production.
The Group includes:
Drax Power Ltd, which operates the largest power station in the UK, based at Selby, North Yorkshire and supplies seven per cent of the country’s electricity needs. The energy firm converted from burning coal to become a predominantly biomass-fueled electricity generator. Drax is the biggest single site renewable generator in the UK and the largest decarbonisation project in Europe.
Haven Power, based in Ipswich, supplies electricity to large Industrial and Commercial sector businesses.
Opus Energy, based in Oxford, Northampton and Cardiff, provides electricity and gas to small and medium sized (SME) businesses.
Drax Biomass, is based in the US and manufactures compressed wood pellets produced from sustainably managed working forests, supplying fuel used by Drax Power Station in North Yorkshire to generate flexible, renewable power for the UK’s homes and businesses.
For more information visit www.drax.com
About C-Capture
C-Capture Ltd utilise their extensive knowledge of CO2 (carbon dioxide) based chemistry and engineering, to develop solvent systems for the removal of CO2 from gas streams with the potential to capture the CO2 in a form suitable for storage, and prevent it from entering the Earth’s atmosphere.
C-Capture‘s proprietary technology aims to remove or ‘scrub’ CO2 from large scale point sources of gas emissions. This is important for a broad range of commercially and environmentally relevant areas.
The low cost, high energy efficiency of C-Capture’s solvents help minimise the cost of CCS implementation and makes electricity generation with CCS a much more affordable, environmentally beneficial process.
C-Capture Ltd is a spin-out company from the Chemistry Department at the University of Leeds, and has attracted support from IP Group, the Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy’s, Energy Entrepreneurs Fund, and the CO2 Capture Project, for development of CO2 capture technology, which has potential in a range of areas, including biogas upgrading, natural gas sweetening and hydrogen production. It was also the National Winner of Shell Springboard 2016, competition for low carbon businesses.
For more information visit www.c-capture.co.uk
About the University of Leeds
The University of Leeds has created more than 100 spin-out companies, with a market capitalisation in excess of £500 million. Seven of these spin-out companies are market listed on AIM, which is more than any other university in the UK. The University is also home to the EPSRC funded Centre for Doctoral Training in Bioenergy, and has extensive experience in energy research through the interdisciplinary Energy Leeds initiative.
The University is preparing to launch its £40m Nexus innovation and enterprise centre later this year. Nexus will provide business and industry with easy access to world-leading academic experts and their ground-breaking research, high quality facilities and cutting edge equipment at the University.
For more information visit www.leeds.ac.uk