-
Latest Drax Electric insights report shows renewables up 32% year-on-year as biomass, wind and solar set new generation records in Q2 2020.
-
Cleanest ever quarter as carbon emissions fall by a third compared to the same period last year, and the carbon intensity of electricity fell to an all-time low of 21 g/kWh on the Spring Bank Holiday.
-
Wholesale power prices down 42% from same quarter last year as demand plummets during lockdown.
-
Cost to balance the grid rises to over £100 million per month as pumped hydro storage and CCGTs called on to manage low demand and high generation from wind and solar sources.
As businesses shut up shop and millions of people were furloughed or working from home during the second quarter of 2020, independent analysis, conducted via Imperial Consultants, by academics from Imperial College London for Drax Electric Insights shows the impact this had on our electricity system.
Lower electricity demand combined with exceptional weather propelled renewables to their greatest ever share of electricity, forcing prices and carbon emissions down to record levels, as well as reducing the need for nuclear and fossil fuel power. At one point renewable electricity sources were providing almost 70% (69.5%) of Britain’s electricity.
The report also highlights how this combination of reduced demand and increased renewable generation meant a record amount of money was spent on keeping the system stable between April and June.
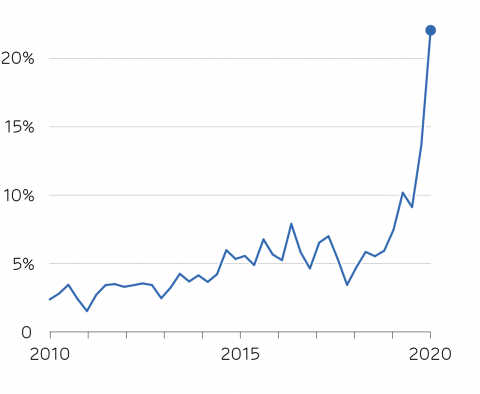
The quarterly-average cost of balancing the power system, expressed as a percentage of the cost of generation [click to view/download]
Dr Iain Staffell of Imperial College London, and lead author of the quarterly Electric Insights reports, said:
“The past few months have given the country a glimpse into the future for our power system, with higher levels of renewable energy and lower demand make for a difficult balancing act. To help the country decarbonise further it is vital that flexible technologies which provide power and system stability play an increasing role in our grid.”
Alongside keeping power supply and demand perfectly in balance, National Grid ESO must also stabilise the system. It does this by ensuring there is not just the right amount of megawatts available to meet demand – but also the right kind of MWs.
During Q2 wind and solar power provided a lot of the electricity required by the grid, which helped the carbon intensity fall to 153 g/kWh averaged over the quarter – its lowest on record. However, these technologies are unable to provide all the services needed to stabilise the system, such as inertia, which is essential for maintaining the grid’s frequency at 50Hz and preventing power cuts.
Whilst wholesale prices fell 42% as a result of falling demand during the period, balancing prices rose from being just 5% of wholesale prices typically over the last decade to 20%, with the cost of the actions taken to stabilise the system averaging £100 million per month during the first half of this year.

Mike Maudsley, Drax Group’s UK Portfolio Generation Director
Mike Maudsley, Drax Group’s UK Portfolio Generation Director, said:
“It has been a challenging time for everyone in the country and for our power system. The last few months have underlined the importance of flexible, low carbon technologies to enable the UK’s power system to evolve and provide the secure and sustainable electricity supplies a zero carbon economy needs.”
ENDS
Top image caption: sourced from Adobe Stock. Branksome Chine Beach, Poole, Dorset, UK during COVID-19 – 1st April 2020.
Editor’s notes
The lockdown shattered power system records:- Electricity output from wind, solar and biomass were each up more than 10% on this quarter last year.
- May was Britain’s first coal-free calendar month since the Industrial Revolution as the country went an unprecedented 67 days without the fuel on the grid.
- Demand fell to its lowest levels this century, falling below 17 GW on the 28th of June.
- The country’s four pumped hydro storage power stations supplied a record 7.9% of power at one stage during the quarter as they helped to balance the system and keep it stable.
For more information visit electricinsights.co.uk or download the full report.
Media contacts:
Aidan Kerr
Drax Group Media Manager
E: aidan.kerr@drax.com
T: 07849 090 368
Selina Williams
Drax Group Media Manager
E: selina.williams@drax.com
T: 07912230393
About Electric Insights
- Electric Insights is commissioned by Drax and delivered by a team of independent academics from Imperial College London, facilitated by the college’s consultancy company – Imperial Consultants. The quarterly report analyses raw data made publicly available by National Grid and Elexon, which run the electricity and balancing market respectively, and Sheffield Solar.
- Electric Insights Quarterly focuses on supply and demand, prices, emissions, the performance of the various generation technologies and the network that connects them.
- The quarterly reports are backed by an interactive website electricinsights.co.uk which provides data from 2009 until the present.
Uniquely, Electric Insights provides real time data about the UK’s transmission grid as well as embedded wind and solar generation which is not available from other sources
About Drax
Drax Group’s purpose is to enable a zero carbon, lower cost energy future and in 2019 announced a world-leading ambition to be carbon negative by 2030, using Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) technology.
Its 2,900-strong employees operate across three principal areas of activity – electricity generation, electricity sales to business customers and compressed wood pellet production.
Power generation:
Drax owns and operates a portfolio of flexible, low carbon and renewable electricity generation assets across Britain. The assets include the UK’s largest power station, based at Selby, North Yorkshire, which supplies five percent of the country’s electricity needs.
Having converted two thirds of Drax Power Station to use sustainable biomass instead of coal it has become the UK’s biggest renewable power generator and the largest decarbonisation project in Europe. It is also where Drax is piloting the groundbreaking negative emissions technology BECCS within its CCUS (Carbon Capture Utilisation and Storage) Incubation Area.
Its pumped storage, hydro and energy from waste assets in Scotland include Cruachan Power Station – a flexible pumped storage facility within the hollowed-out mountain Ben Cruachan. It also owns and operates four gas power stations in England.
Customers:
Through its two B2B energy supply brands, Haven Power and Opus Energy, Drax supplies energy to 250,000 businesses across England, Scotland and Wales.
Pellet production:
Drax owns and operates three pellet mills in the US South which manufacture compressed wood pellets (biomass) produced from sustainably managed working forests. These pellet mills supply around 20% of the biomass used by Drax Power Station in North Yorkshire to generate flexible, renewable power for the UK’s homes and businesses.
For more information visit www.drax.com





















